Did you know that greenhouse farming can yield up to ten times more produce than traditional farming methods? Greenhouse Farming SWOT Analysis is a crucial tool for farmers looking to maximize their crop yields and enhance their business growth. This analysis allows growers to evaluate their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats systematically. Understanding these factors can lead to smarter decision-making and better resource allocation.
Greenhouse farming is a method of growing crops in a controlled environment, allowing farmers to optimize conditions for plant growth and protect them from adverse weather and pests. By employing this technique, farmers can achieve higher yields and better quality produce, ultimately leading to increased profitability. The SWOT analysis framework provides a structured approach to evaluate the internal and external factors that impact greenhouse operations, ensuring that farmers can strategically plan for success.
- Importance of SWOT analysis in farming
- Overview of strengths in greenhouse farming
- Identifying weaknesses to address
- Opportunities for growth in the market
- Threats posed by environmental factors
- Effective management strategies
- Case studies of successful greenhouse operations
- Role of technology in enhancing productivity
- Future trends in greenhouse farming
- Call to action for farmers to implement SWOT analysis
Understanding SWOT Analysis in Greenhouse Farming
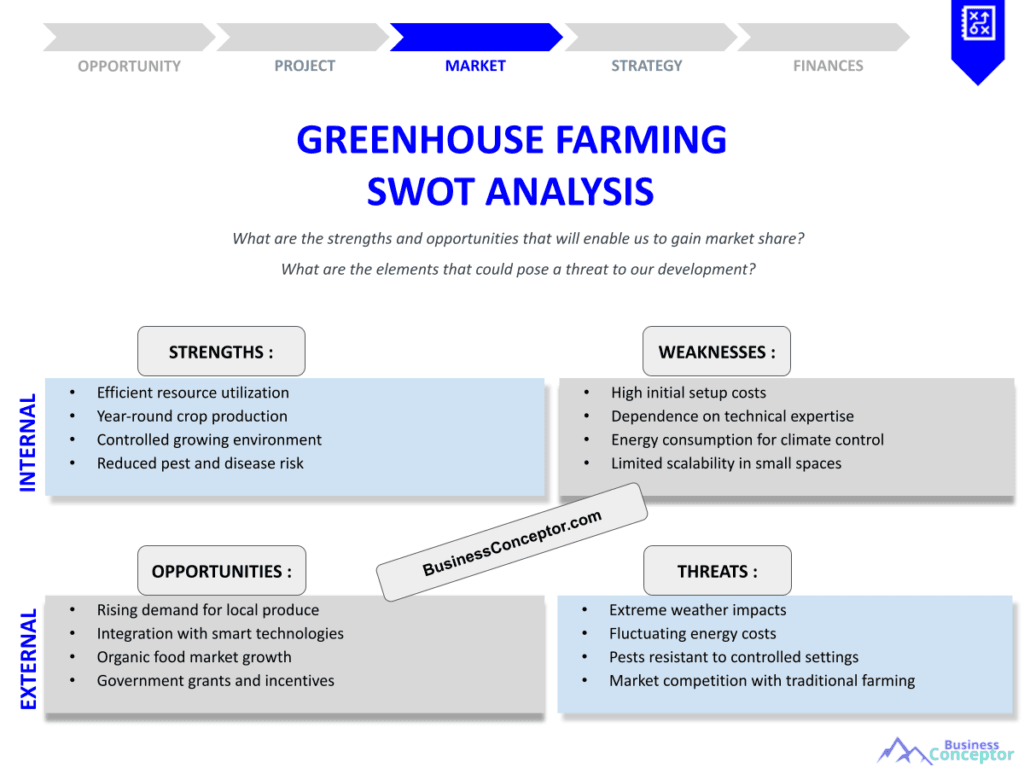
SWOT analysis is a strategic planning technique that helps farmers identify internal and external factors affecting their operations. It’s like having a roadmap to navigate the complexities of greenhouse farming. By analyzing strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, farmers can develop a clear strategy for success.
For example, a greenhouse operation might identify its strength as having access to advanced climate control technologies. Conversely, a weakness could be high labor costs. Opportunities might include the growing demand for organic produce, while threats could involve unpredictable weather patterns affecting crop yields.
Understanding these elements not only helps in strategic planning but also prepares farmers to adapt to changing market dynamics. This foundational understanding sets the stage for a deeper dive into specific aspects of greenhouse farming in the following sections.
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
| Advanced technologies | High labor costs |
| Efficient resource use | Limited market access |
- SWOT analysis aids in strategic planning.
- Recognizing strengths can enhance productivity.
- Addressing weaknesses is crucial for sustainability.
“Success in farming comes from understanding both the soil and the market.”
Strengths of Greenhouse Farming
The strengths of greenhouse farming can significantly impact overall productivity and profitability. One of the main advantages is the ability to control the growing environment, which leads to higher crop yields. This control allows farmers to optimize conditions for photosynthesis and growth, resulting in healthier plants and more abundant harvests. For instance, by regulating temperature and humidity, greenhouse operators can create ideal conditions that extend the growing season and improve plant health.
Additionally, greenhouse farming can utilize sustainable practices, such as water conservation techniques and renewable energy sources. For example, using rainwater collection systems can reduce water costs while ensuring a consistent supply. This not only enhances profitability but also supports environmental sustainability, aligning with the growing consumer demand for eco-friendly practices. Farmers can also implement integrated pest management strategies, reducing chemical usage and promoting healthier crops.
By leveraging these strengths, farmers can position themselves favorably in the market. This strategic advantage can lead to increased sales and customer loyalty, paving the way for future growth. As the industry evolves, maintaining a focus on strengths will be key to staying competitive in the ever-changing landscape of agriculture.
| Opportunities | Market Trends |
|---|---|
| Growing demand for organic produce | Rise of local food movements |
| Technological advancements | Increasing focus on sustainability |
- Controlled environment enhances growth.
- Sustainable practices reduce costs.
- Higher yields lead to better profitability.
– The above steps must be followed rigorously for optimal success.
Weaknesses in Greenhouse Farming
While greenhouse farming has numerous strengths, it also presents certain weaknesses that farmers must address. One common challenge is the initial investment required for setup and technology. High costs can deter potential growers, making it essential to evaluate financing options and return on investment carefully. For instance, purchasing advanced climate control systems or building infrastructure can be a significant financial burden, especially for new farmers.
Furthermore, greenhouse operations often rely on skilled labor, which can be a limitation in certain regions. The availability of trained personnel can impact the operational efficiency and productivity of the greenhouse. Farmers may need to invest in training or consider automation solutions to mitigate this issue. Additionally, managing labor costs effectively is crucial to maintaining profitability in a competitive market.
Addressing these weaknesses proactively is crucial for long-term success. By identifying and planning for these challenges, farmers can create a more resilient business model that withstands market fluctuations. This preparedness not only fosters growth but also ensures sustainability in the face of adversity.
- High initial investment is a common barrier.
- Skilled labor availability can limit operations.
- Proactive planning can mitigate challenges.
“To succeed, always move forward with a clear vision.”
Opportunities in Greenhouse Farming
The opportunities in greenhouse farming are vast and varied. With the rising global demand for fresh produce, especially organic fruits and vegetables, growers have the chance to tap into lucrative markets. Developing a niche market can significantly enhance profitability and brand recognition. For instance, a farmer specializing in heirloom tomatoes could attract customers willing to pay a premium for unique flavors and organic certifications.
Additionally, advancements in technology, such as precision agriculture and smart farming tools, present opportunities for increased efficiency. By adopting these technologies, farmers can optimize their resource use, reduce waste, and improve crop quality. For example, utilizing sensors for monitoring soil moisture can help farmers irrigate more effectively, conserving water while ensuring healthy crop growth.
Capitalizing on these opportunities requires strategic planning and a willingness to adapt. As the market evolves, so too should the approaches farmers take to maximize their business potential. Engaging with local communities and exploring partnerships can also open doors to new markets and customer bases, ensuring long-term sustainability.
| Opportunities | Market Trends |
|---|---|
| Growing demand for organic produce | Rise of local food movements |
| Technological advancements | Increasing focus on sustainability |
- Identify niche markets for growth.
- Invest in technology for efficiency.
- Stay updated on market trends.
– The above steps must be followed rigorously for optimal success.
Threats in Greenhouse Farming
Despite the opportunities, greenhouse farmers face several threats that can jeopardize their success. Climate change is a significant concern, as unpredictable weather patterns can adversely affect crop yields. Farmers must be prepared to adapt their strategies to mitigate these risks. For example, implementing robust irrigation systems can help ensure crops receive adequate water during dry spells, while protective measures like shading can safeguard plants from extreme heat.
Additionally, competition in the market is fierce. With more growers entering the field, distinguishing one’s products becomes essential. Farmers may need to invest in marketing and branding to stand out and attract customers. Utilizing social media and local farmers’ markets can enhance visibility and strengthen customer relationships, providing a competitive edge.
Understanding and addressing these threats is vital for maintaining a competitive edge. By developing contingency plans and diversifying crops, farmers can safeguard their operations against potential setbacks. This proactive approach not only enhances resilience but also fosters confidence in navigating the challenges of the agricultural landscape.
| Threats | Risk Factors |
|---|---|
| Climate change | Unpredictable weather patterns |
| Market competition | Price fluctuations |
- Develop contingency plans for climate risks.
- Invest in marketing strategies.
- Diversify crops to reduce dependency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, conducting a SWOT analysis for greenhouse farming is crucial for maximizing crop yields and ensuring business growth. By understanding strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, farmers can make informed decisions that lead to successful operations. This structured approach helps identify areas for improvement and allows for strategic planning that aligns with market demands.
As the agricultural landscape continues to evolve, those who embrace the principles of SWOT analysis will be better equipped to navigate challenges and seize new opportunities. Whether it’s leveraging technology to enhance productivity or adapting to consumer trends, farmers must remain agile and proactive in their strategies.
Now is the time to take action! If you’re involved in greenhouse farming, start your SWOT analysis today to unlock your operation’s full potential. The insights gained can pave the way for increased profitability and sustainability in your farming endeavors.
| Summary | Action Steps |
|---|---|
| SWOT analysis is essential for strategic planning. | Implement findings for better decision-making. |
| Addressing weaknesses and threats is crucial. | Stay adaptable to market changes. |
FAQ Section
What is SWOT analysis in greenhouse farming?
SWOT analysis is a strategic tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in greenhouse farming, helping farmers make informed decisions.
How can strengths in greenhouse farming be leveraged?
Farmers can leverage strengths such as advanced technologies and controlled environments to maximize crop yields and profitability.
What are common weaknesses in greenhouse farming?
Common weaknesses include high initial investment costs and reliance on skilled labor, which can limit operational efficiency.
What opportunities exist for greenhouse farmers?
Opportunities include the growing demand for organic produce and advancements in farming technologies that enhance efficiency.
What threats do greenhouse farmers face?
Greenhouse farmers face threats like climate change, market competition, and fluctuating prices that can impact profitability.
How does climate change affect greenhouse farming?
Climate change can lead to unpredictable weather patterns, affecting crop yields and requiring farmers to adapt their strategies.
What role does technology play in greenhouse farming?
Technology plays a significant role by improving resource efficiency, enhancing crop quality, and reducing operational costs.
Why is marketing important for greenhouse farmers?
Marketing is crucial for differentiating products in a competitive market and attracting customers to increase sales.
How can farmers mitigate risks associated with threats?
Farmers can mitigate risks by developing contingency plans, diversifying crops, and staying informed about market trends.
What is the future of greenhouse farming?
The future of greenhouse farming looks promising with increasing demand for fresh produce and advancements in sustainable farming practices.
Innovative Practices in Greenhouse Farming
As greenhouse farming continues to evolve, innovative practices are emerging that can significantly enhance productivity and sustainability. One such practice is the integration of hydroponics and aeroponics, which allow farmers to grow plants without soil, using nutrient-rich water instead. This method not only conserves water but also accelerates plant growth, leading to faster harvest cycles.
Additionally, implementing vertical farming techniques within greenhouses maximizes space utilization. By stacking layers of crops, farmers can produce more food in a smaller footprint, which is particularly beneficial in urban areas where land is scarce. This innovation aligns with the trend of local food production, reducing transportation costs and ensuring fresher produce for consumers.
Moreover, utilizing renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, can significantly decrease operational costs while promoting sustainability. By harnessing natural energy, farmers can power their greenhouses and reduce their carbon footprint, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers. These innovative practices not only improve efficiency but also contribute to the long-term viability of greenhouse farming.
| Innovative Practices | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Hydroponics and Aeroponics | Faster growth, water conservation |
| Vertical Farming | Maximized space utilization, local production |
- Explore hydroponics and aeroponics for efficiency.
- Consider vertical farming to maximize space.
- Implement renewable energy solutions for sustainability.
– The above steps must be followed rigorously for optimal success.
Practical Tips for Greenhouse Farmers
For those engaged in greenhouse farming, applying practical tips can lead to improved outcomes and enhanced profitability. First and foremost, regular monitoring of environmental conditions is essential. Utilizing sensors for temperature, humidity, and soil moisture can provide valuable data, allowing farmers to make timely adjustments to optimize growing conditions. This proactive approach helps prevent issues before they escalate, ensuring healthier plants and higher yields.
Additionally, diversifying crop selection can mitigate risks associated with market fluctuations. By growing a variety of crops, farmers can protect themselves from the impacts of poor sales or crop failures in any single area. For instance, if one crop experiences a downturn in demand, others may compensate, stabilizing overall income.
Finally, engaging with local communities through farmers’ markets and social media can strengthen customer relationships and build brand loyalty. By sharing stories about their farming practices and the benefits of greenhouse farming, growers can connect with consumers on a personal level, fostering a loyal customer base that supports their operations.
- Regularly monitor environmental conditions.
- Diversify crop selection to reduce risks.
- Engage with local communities for brand loyalty.
“Success comes to those who persevere.”
By implementing these practical tips, greenhouse farmers can enhance their operations, ensuring greater resilience and profitability in the competitive agricultural landscape.
Conclusion
In summary, conducting a SWOT analysis for greenhouse farming is essential for maximizing crop yields and fostering business growth. By understanding the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, farmers can make informed decisions that lead to successful and sustainable operations. As we explored, leveraging innovative practices, engaging with local communities, and maintaining a proactive approach can significantly enhance the overall effectiveness of greenhouse operations.
To further assist you in your greenhouse farming journey, consider utilizing a comprehensive Greenhouse Farming Business Plan Template that provides a solid foundation for your business strategy. Additionally, you might find the following articles helpful:
- Article 1 about Greenhouse Farming Profitability: What You Need to Know
- Article 2 about Greenhouse Farming Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide
- Article 3 about Financial Planning for Greenhouse Farming: A Detailed Guide with Examples
- Article 4 about Building a Greenhouse Farming Business: Complete Guide with Examples
- Article 5 about Create a Marketing Plan for Your Greenhouse Farming Business (+ Example)
- Article 6 about How to Create a Business Model Canvas for Greenhouse Farming: Examples and Tips
- Article 7 about Customer Segments for Greenhouse Farming: Who Are Your Potential Customers?
- Article 8 about How Much Does It Cost to Start a Greenhouse Farming Business?
- Article 9 about Greenhouse Farming Feasibility Study: Expert Insights
- Article 10 about Ultimate Guide to Greenhouse Farming Risk Management
- Article 11 about Greenhouse Farming Competition Study: Detailed Insights
- Article 12 about Greenhouse Farming Legal Considerations: Ultimate Guide
- Article 13 about Exploring Funding Options for Greenhouse Farming
- Article 14 about Greenhouse Farming Growth Strategies: Scaling Guide
FAQ Section
What is greenhouse farming?
Greenhouse farming refers to the practice of growing crops in a controlled environment, allowing for optimized growth conditions and protection from external elements.
How can SWOT analysis help greenhouse farmers?
SWOT analysis helps greenhouse farmers identify their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, enabling them to make informed decisions and strategic plans.
What are the main strengths of greenhouse farming?
Key strengths include the ability to control environmental conditions, leading to higher crop yields and the potential for sustainable practices that attract eco-conscious consumers.
What weaknesses should greenhouse farmers be aware of?
Common weaknesses involve high initial setup costs and reliance on skilled labor, which can impact operational efficiency.
What opportunities exist for growth in greenhouse farming?
Opportunities include rising demand for organic produce, advancements in agricultural technology, and the potential for niche market development.
What threats do greenhouse farmers face in today’s market?
Threats include the impacts of climate change, market competition, and fluctuating consumer preferences that can affect profitability.
How does technology improve greenhouse farming?
Technology enhances greenhouse farming by improving resource efficiency, reducing costs, and facilitating better monitoring of plant health and environmental conditions.
Why is customer engagement important for greenhouse farmers?
Engaging with customers builds loyalty and helps farmers understand consumer preferences, which can lead to better marketing strategies and product offerings.
How can farmers mitigate risks in greenhouse farming?
Farmers can mitigate risks by diversifying crop production, developing contingency plans for adverse weather, and staying informed about market trends.
What is the future outlook for greenhouse farming?
The future of greenhouse farming appears bright, with increasing demand for fresh produce, innovative technologies, and sustainable practices paving the way for growth and success.