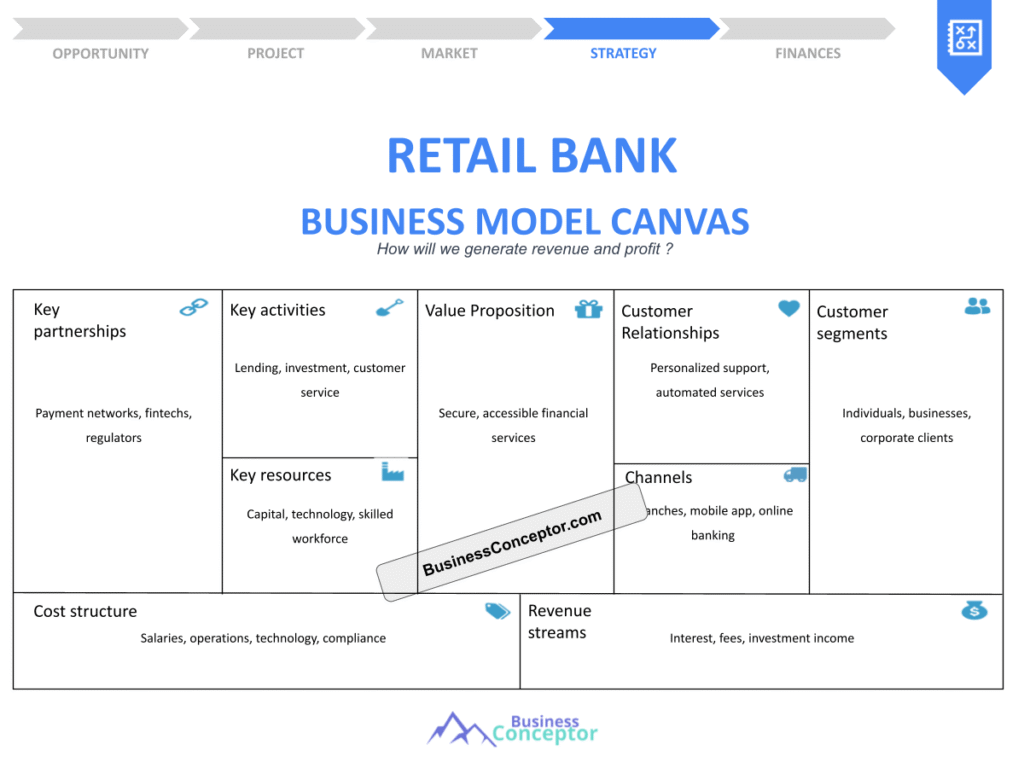
Did you know that nearly 70% of retail banks are currently re-evaluating their business models to adapt to the digital age? This statistic highlights the importance of a solid Retail Bank Business Model Canvas in today’s fast-paced financial environment. In simple terms, a business model canvas is a strategic tool that allows banks to visualize and understand their operations, customer relationships, and revenue streams in a clear and concise format. It’s a game-changer for retail banks aiming to innovate and grow.
- Understand the components of a business model canvas.
- Learn how to identify customer segments.
- Explore value propositions tailored for banking.
- Analyze key resources and activities in retail banking.
- Discover revenue streams and cost structures.
- Examine customer relationships and channels.
- Review real-life examples of successful banking models.
- Apply the business model canvas to your banking strategy.
- Adapt to changes in the banking landscape.
- Prepare for future challenges in retail banking.
Understanding the Business Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas is more than just a diagram; it’s a roadmap for retail banks. It helps visualize how a bank creates, delivers, and captures value. This tool can be especially useful for banks looking to innovate or pivot in response to market changes. Each segment of the canvas is interconnected, meaning changes in one area can impact others.
For example, consider a bank that wants to introduce a new mobile banking app. This decision affects customer segments, value propositions, key activities, and potentially revenue streams. It’s essential to consider these connections when creating a business model canvas.
In summary, the Business Model Canvas provides a comprehensive view of a bank’s strategy and operations, laying the groundwork for further exploration of each component in the following sections.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Customer Segments | Different groups of customers targeted by the bank |
| Value Proposition | Unique offerings that meet customer needs |
| Channels | How the bank delivers services to customers |
| Customer Relationships | The nature of interactions with customers |
| Revenue Streams | Sources of income for the bank |
| Key Resources | Essential assets required for operations |
| Key Activities | Core activities necessary to deliver value |
| Cost Structure | Major expenses incurred by the bank |
- Understand the importance of the Business Model Canvas.
- Recognize the interconnectedness of its components.
- Explore how each part contributes to the overall strategy.
- "A great strategy is a living document that evolves as you do."
Identifying Customer Segments
Understanding your customer segments is critical in the retail banking sector. These are the various groups of people or organizations that a bank aims to reach and serve. For example, banks might target individual consumers, small businesses, or corporate clients. Identifying these segments allows banks to tailor their services and marketing strategies to better meet customer needs.
Statistics show that banks focusing on specific customer segments often outperform those with a one-size-fits-all approach. By analyzing customer needs, preferences, and behaviors, banks can provide personalized experiences, which are increasingly important in today’s competitive landscape. This segmentation allows banks to optimize their offerings and improve customer satisfaction.
By the end of this section, you’ll see how identifying customer segments directly influences the value propositions and marketing channels you choose, ensuring a more effective approach to serving your customers.
- Conduct market research to understand demographics.
- Analyze customer behavior and preferences.
- Segment customers based on their needs and value to the bank.
- The above steps must be followed rigorously for optimal success.
Crafting a Compelling Value Proposition
A strong value proposition is essential for attracting and retaining customers in retail banking. It’s the promise of value that a bank delivers to its customers, distinguishing it from competitors. For example, a bank may offer lower fees, better interest rates, or superior customer service as part of its value proposition.
To create a compelling value proposition, banks must understand what their customers truly value. This could involve gathering feedback through surveys or analyzing competitors. A well-defined value proposition not only attracts customers but also fosters loyalty, as customers feel understood and valued. The importance of aligning your offerings with customer expectations cannot be overstated.
By focusing on crafting a unique value proposition, banks can better align their services with customer expectations, leading to increased satisfaction and retention. This connection to customer needs is what makes a value proposition truly effective.
- Value propositions differentiate banks from competitors.
- Understanding customer needs is key to crafting value.
- A compelling value proposition fosters customer loyalty.
- "To succeed, always move forward with a clear vision."
Analyzing Key Resources
In the retail banking sector, key resources are the assets and capabilities that enable banks to deliver value to customers. These can include physical assets, such as branches and ATMs, as well as intangible assets like brand reputation and customer data. Understanding your key resources is crucial for effective resource allocation and operational efficiency.
For instance, if a bank invests heavily in digital infrastructure, it may enhance customer experience and streamline operations. Conversely, neglecting key resources can hinder a bank’s ability to compete effectively. Regularly assessing these resources allows banks to identify areas where improvements can be made, ultimately leading to better service delivery and customer satisfaction.
In summary, analyzing key resources helps banks leverage their strengths and address weaknesses in their business model, ensuring they remain competitive in a rapidly changing market.
| Resource Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Physical Assets | Branches, ATMs, and technology infrastructure |
| Human Resources | Skilled employees and management teams |
| Intellectual Property | Patents, trademarks, and customer data |
- Assess the effectiveness of current resources.
- Invest in technology for better customer service.
- Train employees to enhance customer interactions.
- "A great resource is one that evolves with the needs of the market."
Understanding Revenue Streams
Revenue streams are the various sources from which a bank generates income. These can include interest from loans, fees for services, and investment income. Understanding these streams is essential for sustaining profitability and growth. Banks that diversify their revenue streams can better manage risks associated with fluctuating interest rates and changing market conditions.
For example, a bank that diversifies its revenue streams by offering investment services can mitigate risks associated with relying solely on loan interest. Additionally, analyzing the performance of different revenue streams helps banks make informed decisions about where to focus their efforts and how to innovate their service offerings.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of revenue streams allows banks to adapt their strategies and improve financial performance, ensuring long-term sustainability in a competitive marketplace.
| Revenue Source | Description |
|---|---|
| Interest Income | Earnings from loans and credit products |
| Fees and Commissions | Charges for services like account maintenance |
| Investment Income | Profits from investments and securities |
- Review current revenue streams for performance.
- Explore new services that can generate income.
- Monitor market trends to adjust pricing strategies.
Managing Cost Structure
Understanding the cost structure is vital for any retail bank. It encompasses all the costs incurred to operate the bank, including fixed and variable costs. By analyzing these costs, banks can identify areas for improvement and efficiency gains, which is essential for maintaining profitability.
For instance, a bank might find that operational costs are too high due to outdated technology or inefficient processes. By investing in modern technology, a bank can reduce costs and improve service delivery. Additionally, understanding the cost structure helps banks set competitive pricing for their products and services, ensuring they remain attractive to customers.
In summary, effective cost management is essential for maintaining profitability and ensuring long-term sustainability in the competitive landscape of retail banking. By regularly reviewing and optimizing their cost structures, banks can position themselves for future success.
| Cost Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Fixed Costs | Rent, salaries, and insurance |
| Variable Costs | Marketing expenses and technology upgrades |
- Conduct a cost analysis to identify areas for reduction.
- Invest in technology to automate processes.
- Review supplier contracts for potential savings.
Building Customer Relationships
Customer relationships are crucial in retail banking, as they influence customer loyalty and retention. Banks must strive to build strong, trust-based relationships with their customers. This can be achieved through personalized service, effective communication, and reliable support.
For example, offering financial advice or personalized product recommendations can enhance customer satisfaction. Banks can also utilize technology, such as CRM systems, to track customer interactions and preferences, allowing for a more tailored approach to customer service. By fostering strong relationships, banks can improve customer loyalty and reduce churn.
In conclusion, building strong customer relationships is essential for long-term success in the retail banking sector. The ability to connect with customers on a personal level not only enhances their experience but also strengthens the bank’s reputation in the market.
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Personalization | Tailoring services to individual customer needs |
| Communication | Regular updates and feedback channels |
- Use CRM systems for better customer insights.
- Offer personalized services to enhance satisfaction.
- Maintain open lines of communication with customers.
Leveraging Channels
Channels are the means through which banks deliver value to their customers. These can include physical branches, online platforms, and mobile apps. Understanding how customers prefer to engage with the bank is essential for optimizing these channels and enhancing the overall customer experience.
For instance, with the rise of digital banking, many customers prefer online services over visiting branches. By investing in user-friendly digital platforms, banks can meet customer preferences and improve service delivery. Additionally, analyzing customer feedback regarding their preferred channels can help banks refine their offerings and enhance customer satisfaction.
In summary, leveraging the right channels ensures that banks can effectively reach their customers and provide a seamless banking experience. Adapting to customer preferences not only boosts engagement but also solidifies the bank’s position in the competitive retail banking landscape.
| Channel Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Branches | Traditional banking locations for in-person services |
| Digital Platforms | Websites and mobile apps for online banking |
- Analyze customer preferences for channel usage.
- Invest in user-friendly digital platforms.
- Train staff to improve in-branch customer service.
Adapting to Changes in the Banking Landscape
The banking landscape is constantly evolving due to technological advancements and changing customer expectations. Retail banks must remain adaptable to thrive in this environment. This includes embracing innovation, such as integrating fintech solutions and enhancing digital services.
For example, banks that adopt AI-driven analytics can better understand customer behavior and preferences, leading to improved service offerings. Staying informed about industry trends and being proactive in addressing challenges is essential for long-term success. By fostering a culture of adaptability, banks can navigate the complexities of the market and continue to meet customer needs.
In summary, adaptability is key for retail banks to remain competitive and meet the needs of their customers. By continuously evolving and innovating, banks can position themselves as leaders in the financial services industry.
| Adaptation Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Embrace Innovation | Integrate new technologies and solutions |
| Monitor Trends | Stay informed about market changes and customer preferences |
- Monitor industry trends for potential impacts on banking.
- Embrace technology to enhance service delivery.
- Foster a culture of innovation within the bank.
Conclusion
In summary, creating a Retail Bank Business Model Canvas is a vital process for understanding and optimizing your bank’s operations. By thoroughly analyzing each component—customer segments, value propositions, key resources, revenue streams, cost structure, customer relationships, channels, and adaptability—you can build a robust strategy that positions your bank for success.
To further enhance your banking strategy, consider exploring our Retail Bank Business Plan Template. It’s a comprehensive resource designed to assist you in developing a solid business plan.
Additionally, check out our articles for more insights on retail banking:
- SWOT Analysis for Retail Bank: Maximizing Business Potential
- Retail Bank Profitability: Strategies for a Profitable Business
- Developing a Business Plan for Your Retail Bank: Comprehensive Guide
- Crafting a Financial Plan for Your Retail Bank: Essential Steps (+ Example)
- How to Start a Retail Bank: Complete Guide with Example
- Building a Retail Bank Marketing Plan: Strategies and Examples
- Customer Segments in Retail Banking: Examples and Strategies
- How Much Does It Cost to Operate a Retail Bank?
- How to Calculate the Feasibility Study for Retail Bank?
- How to Calculate Risks in Retail Bank Management?
- How to Analyze Competition for Retail Bank?
- How to Address Legal Considerations in Retail Bank?
- How to Choose the Right Funding for Retail Bank?
- How to Implement Growth Strategies for Retail Bank
FAQ Section
What is a Retail Bank Business Model Canvas?
A Retail Bank Business Model Canvas is a strategic framework that outlines how a bank creates, delivers, and captures value in the retail banking sector. It helps visualize the bank’s operations and customer interactions.
How can customer segments be identified in banking?
Customer segments can be identified through thorough market research, analysis of customer behavior, and segmentation based on individual needs and values, ensuring that the bank can tailor its services effectively.
What role does the value proposition play in retail banking?
The value proposition is the unique value a bank promises to deliver to its customers, setting it apart from competitors and helping to attract and retain clients through tailored offerings.
Why is it important to analyze key resources?
Analyzing key resources allows banks to leverage their strengths and improve operational efficiency, which is essential for delivering high-quality services to customers.
How do revenue streams impact a bank’s profitability?
Revenue streams are vital sources of income for banks. Diversifying these streams can help mitigate risks and enhance overall profitability, ensuring financial stability.
What strategies can enhance customer relationships in banking?
Enhancing customer relationships can be achieved through personalized services, effective communication, and utilizing CRM systems to track customer preferences and interactions, fostering trust and loyalty.
How can channels be optimized for better customer engagement?
Channels can be optimized by analyzing customer preferences, investing in user-friendly digital platforms, and improving in-branch service to meet customer needs effectively.
Why is adaptability crucial for retail banks?
Adaptability is essential for retail banks to navigate changes in the banking landscape, including technological advancements and evolving customer expectations, ensuring they remain competitive and relevant.
What are the key components of a retail bank’s cost structure?
The cost structure includes both fixed costs (like rent and salaries) and variable costs (such as marketing and technology upgrades), which are critical for maintaining profitability.
How can banks stay informed about industry trends?
Banks can stay informed about industry trends by monitoring market changes, engaging with customers, and conducting regular assessments of their strategies and operations.