Did you know that greenhouse farming can increase crop yield by up to 30% compared to traditional farming? It’s a game-changer in agriculture, and understanding the Greenhouse Farming Business Model Canvas can set you on the path to success. This strategic tool helps you visualize and design your business model, ensuring that all essential components are aligned for optimal performance. In this article, we’ll explore how to create your own business model canvas for greenhouse farming, complete with examples and valuable tips to help you thrive.
- Understand the components of a business model canvas.
- Identify customer segments and value propositions.
- Analyze revenue streams and cost structures.
- Explore key partnerships in greenhouse farming.
- Learn about market analysis and customer relationships.
- Discover practical tips for implementing your business model.
- Review case studies of successful greenhouse operations.
- Understand the importance of financial projections.
- Explore risks and challenges in greenhouse farming.
- Get inspired with real-world examples and actionable advice.
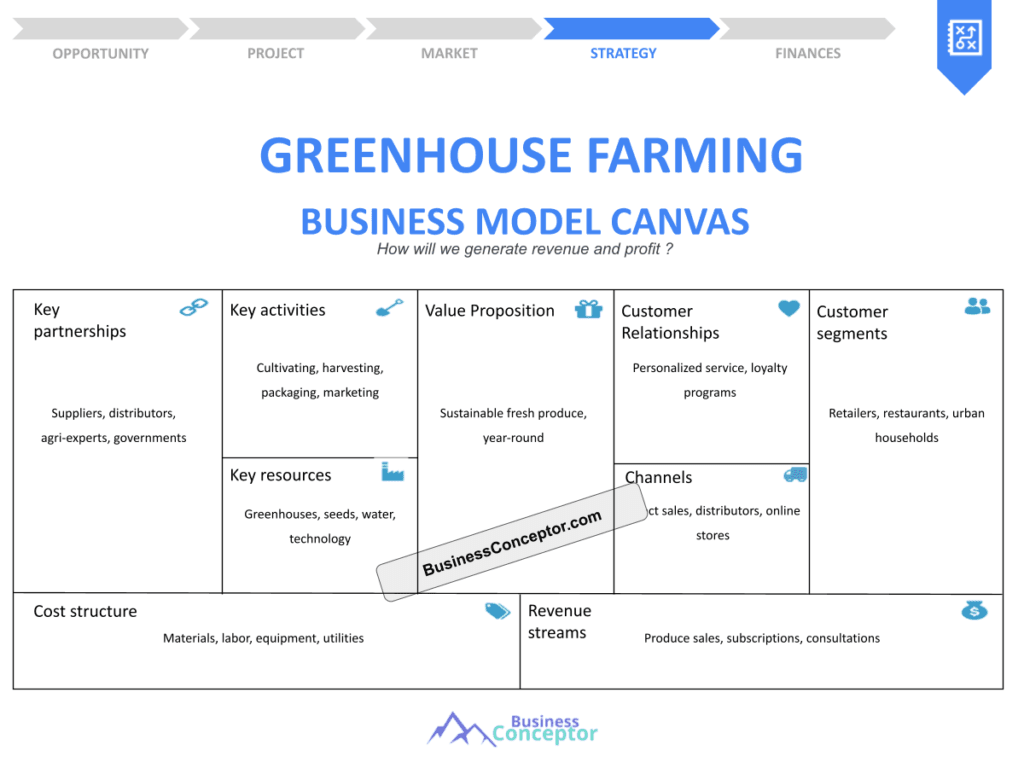
Understanding the Business Model Canvas for Greenhouse Farming
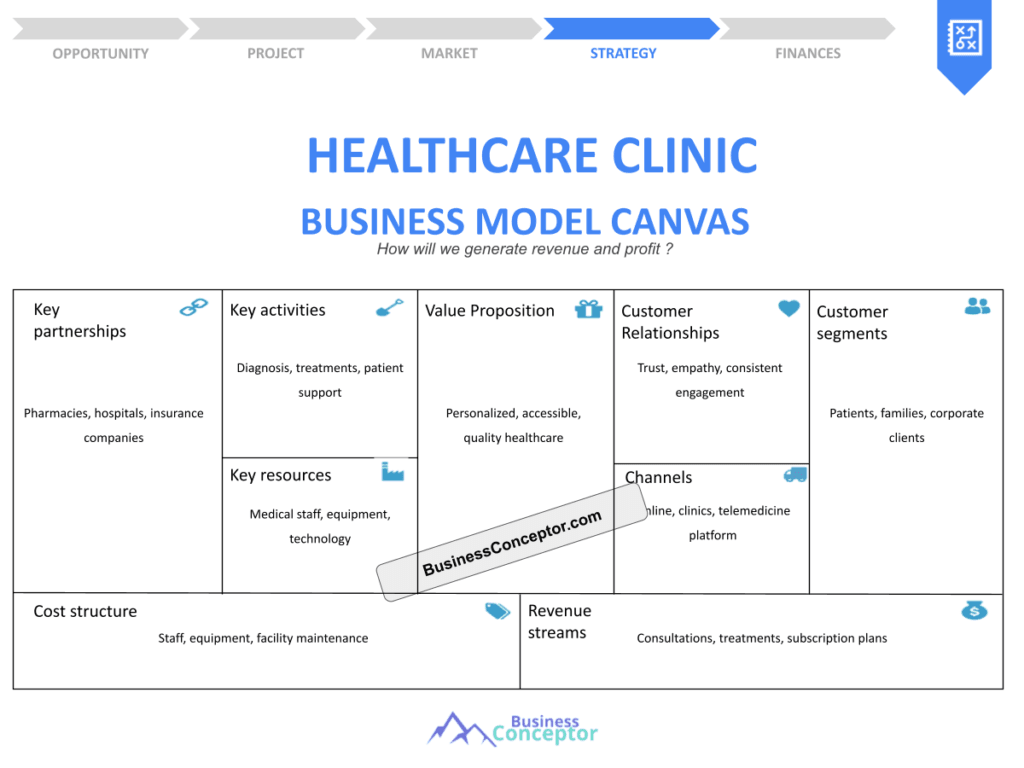
The Business Model Canvas is a strategic management tool that provides a visual framework for developing or documenting a business model. For greenhouse farming, it helps you map out your entire business structure on a single page, which is crucial for clarity and focus. This model consists of nine building blocks that cover all aspects of your business, from customer segments to cost structures.
Each block of the canvas plays a vital role. For example, the customer segments block helps you identify who your target customers are, whether they are local restaurants, grocery stores, or direct consumers. The value proposition block allows you to articulate what makes your greenhouse products unique, such as organic certification or sustainable practices.
By using the Business Model Canvas, greenhouse farmers can effectively communicate their business ideas, attract investors, and streamline their operations. Let’s dive deeper into each component of the canvas in the next section.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Customer Segments | Who are your customers? |
| Value Proposition | What unique value do you offer? |
| Revenue Streams | How will you make money? |
| Key Activities | What activities are crucial for your business? |
| Key Resources | What resources do you need? |
| Key Partnerships | Who will you collaborate with? |
| Cost Structure | What are your main costs? |
| Customer Relationships | How will you interact with customers? |
| Channels | How will you deliver your products? |
- Understand the Business Model Canvas components
- Identify target customers
- Define unique value propositions
- Analyze revenue streams
- Map key activities and resources
– “A goal without a plan is just a wish.”
Identifying Customer Segments in Greenhouse Farming
Identifying customer segments is crucial for any business, especially in greenhouse farming. It involves understanding who your potential buyers are and what they want. By segmenting your market, you can tailor your products and marketing strategies to meet the specific needs of each group.
For instance, you might target local restaurants that prioritize fresh, organic ingredients. Alternatively, you could cater to health-conscious consumers looking for nutritious produce at farmers’ markets. Understanding these segments allows you to create customized marketing campaigns and establish stronger connections with your customers.
As you refine your customer segments, remember to gather feedback and adjust your offerings accordingly. This will ensure that you remain relevant and competitive in the market. Let’s explore the value propositions that resonate with these segments in the next section.
- Research local market demands.
- Identify key customer demographics.
- Create customer personas to tailor marketing.
– The above steps must be followed rigorously for optimal success.
Crafting Your Value Proposition for Greenhouse Products
Your value proposition is what sets your greenhouse business apart from the competition. It’s about clearly articulating why customers should choose your products over others. This can include factors like quality, sustainability, and innovation.
For example, if you grow heirloom tomatoes, your value proposition might emphasize their unique flavor and organic cultivation methods. Highlighting such aspects can attract a niche market willing to pay a premium for superior products.
To effectively communicate your value proposition, consider using storytelling in your marketing efforts. Share your farming journey, your commitment to sustainability, or the health benefits of your produce. This personal touch can significantly enhance customer loyalty.
- Define unique selling points
- Focus on quality and sustainability
- Use storytelling in marketing
– “Differentiate or die – stand out in the market!”
Exploring Revenue Streams in Greenhouse Farming
Revenue streams are essential for understanding how your greenhouse business will generate income. This could come from direct sales at farmers’ markets, subscription services, or even selling seedlings and plants to other growers.
For instance, many successful greenhouse farmers offer CSA (Community Supported Agriculture) programs, where customers pay upfront for a share of the harvest. This not only secures funds early in the season but also fosters a community around your farm.
Diversifying your revenue streams can help mitigate risks and stabilize your income. Explore additional opportunities like workshops, tours, or partnering with local restaurants for exclusive supply agreements.
| Revenue Stream | Description |
|---|---|
| Direct Sales | Selling produce directly to consumers |
| Subscription Services | Offering CSA programs to secure upfront payments |
| Workshops | Educating others about greenhouse practices |
- Explore direct sales options
- Consider subscription models
- Diversify income sources through workshops
– “The more you diversify, the more secure your income becomes.”
Key Partnerships for Successful Greenhouse Farming
In greenhouse farming, building key partnerships can greatly enhance your business operations. Collaborating with suppliers, distributors, and local businesses can create a robust support network.
For example, partnering with local garden centers can help you reach a wider audience for your seedlings. Additionally, collaborating with agricultural extension services can provide you with valuable resources and expertise to improve your farming practices.
Establishing strong relationships with other farmers can also lead to shared resources and knowledge. Networking with local agricultural organizations can open doors to new opportunities and funding sources.
| Partnership Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Suppliers | Access to quality materials at better prices |
| Local Businesses | Increased visibility and customer base |
| Agricultural Organizations | Networking and resource sharing |
- Identify potential suppliers
- Network with local businesses
- Join agricultural organizations
Cost Structure in Greenhouse Farming
Understanding your cost structure is critical for the sustainability of your greenhouse business. This includes both fixed costs, like land and equipment, and variable costs, such as labor and utilities.
For instance, implementing energy-efficient technologies can help reduce utility costs in the long run. It’s also essential to keep track of your expenses meticulously to ensure profitability. By closely monitoring your cost structure, you can identify areas where you might be overspending and make necessary adjustments.
Regularly reviewing your cost structure can help identify areas where you can cut costs or invest in more efficient practices. This proactive approach can significantly impact your bottom line and help you maintain a competitive edge in the market.
| Cost Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Fixed Costs | Expenses that do not change with production levels |
| Variable Costs | Expenses that vary based on production levels |
- Analyze fixed and variable costs
- Implement cost-cutting measures
- Regularly review expenses for optimization
– “Keeping a close eye on costs is the key to profitability.”
Implementing Your Greenhouse Business Model Canvas
Once you’ve developed your Business Model Canvas, the next step is implementation. This involves translating your strategic plan into actionable steps that guide your daily operations.
Begin by setting clear goals and objectives based on your canvas. For example, if your value proposition emphasizes organic produce, ensure that all farming practices align with organic standards. This alignment will help you build credibility with your customers and strengthen your brand.
Additionally, regularly review and adjust your business model as needed. The agricultural landscape can change rapidly, and being adaptable is key to long-term success. By staying flexible and open to change, you can ensure that your greenhouse business remains relevant and competitive.
| Implementation Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Set Clear Goals | Establish specific, measurable objectives |
| Align Operations | Ensure daily practices reflect business model |
- Set actionable goals
- Align practices with your model
- Regularly review and adjust
Measuring Success in Your Greenhouse Business
Measuring success is vital for any business, and greenhouse farming is no exception. Key performance indicators (KPIs) can help you track progress and make informed decisions about your operations.
Some important KPIs to consider include crop yield per square foot, customer acquisition costs, and overall profitability. Regularly analyzing these metrics can help you identify trends and areas for improvement, enabling you to refine your strategies and enhance your business performance.
By establishing a robust measurement system, you can ensure that your greenhouse business remains on track to meet its goals and objectives. This proactive approach will help you adapt and thrive in the competitive agricultural market, ensuring long-term sustainability.
| KPI | Importance |
|---|---|
| Crop Yield | Measures efficiency and productivity |
| Customer Acquisition | Assesses marketing effectiveness |
- Identify relevant KPIs
- Regularly analyze performance metrics
- Adjust strategies based on findings
– “What gets measured gets managed!”
Overcoming Challenges in Greenhouse Farming
Like any business, greenhouse farming comes with its challenges. From weather fluctuations to pest management, it’s essential to be prepared for the unexpected. Understanding these challenges and having strategies in place can make a significant difference in your success.
One practical tip is to invest in technology that can help monitor and control environmental conditions within your greenhouse. For example, automated irrigation systems can save time and resources while ensuring optimal plant health. Implementing such technologies not only improves efficiency but also enhances the overall quality of your produce.
Additionally, building a supportive network of fellow farmers can provide valuable insights and resources for overcoming common challenges. Remember, adaptability and resilience are key to success in this industry. By staying informed and connected, you can navigate obstacles more effectively and maintain a thriving greenhouse business.
– “Challenges are what make life interesting; overcoming them is what makes life meaningful.”
- Invest in technology for monitoring conditions
- Build a network of support with other farmers
- Stay adaptable to changing circumstances
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the Greenhouse Farming Business Model Canvas is essential for establishing a successful greenhouse venture. By understanding each component—from customer segments to revenue streams—you can create a well-rounded business strategy that drives growth and profitability. To help you get started, consider utilizing a Greenhouse Farming Business Plan Template that provides a comprehensive framework for your planning needs.
To further enhance your knowledge and strategy, check out these informative articles on greenhouse farming:
- SWOT Analysis for Greenhouse Farming: Maximizing Crop Yields and Business Growth
- Greenhouse Farming Profitability: What You Need to Know
- Greenhouse Farming Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide
- Financial Planning for Greenhouse Farming: A Detailed Guide with Examples
- Building a Greenhouse Farming Business: Complete Guide with Examples
- Create a Marketing Plan for Your Greenhouse Farming Business (+ Example)
- Customer Segments for Greenhouse Farming: Who Are Your Potential Customers?
- How Much Does It Cost to Start a Greenhouse Farming Business?
- Greenhouse Farming Feasibility Study: Expert Insights
- Ultimate Guide to Greenhouse Farming Risk Management
- Greenhouse Farming Competition Study: Detailed Insights
- Greenhouse Farming Legal Considerations: Ultimate Guide
- Exploring Funding Options for Greenhouse Farming
- Greenhouse Farming Growth Strategies: Scaling Guide
FAQ
What is a Greenhouse Farming Business Model Canvas?
A Greenhouse Farming Business Model Canvas is a strategic tool that helps visualize the key components of a greenhouse business, including customer segments, value propositions, and revenue streams.
How do I identify customer segments for my greenhouse business?
To identify customer segments, research local market demands, analyze demographics, and create detailed customer personas to tailor your marketing strategies effectively.
What are some common revenue streams in greenhouse farming?
Common revenue streams include direct sales of produce, subscription services like Community Supported Agriculture (CSA), and educational workshops on greenhouse practices.
Why is a value proposition important in greenhouse farming?
A value proposition differentiates your greenhouse products from competitors and communicates the unique benefits to your target audience, helping to attract and retain customers.
How can I measure success in my greenhouse business?
Measuring success involves establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) such as crop yield, customer acquisition costs, and overall profitability to track your business performance.
What challenges might I face in greenhouse farming?
Challenges in greenhouse farming can include weather fluctuations, pest management, and market competition. Being prepared with strategies to address these issues is crucial.
How can technology help in greenhouse farming?
Investing in technology, such as automated irrigation systems and environmental monitoring tools, can enhance efficiency, improve crop quality, and help you manage resources effectively.
What are key partnerships in greenhouse farming?
Key partnerships can include suppliers for seeds and materials, local businesses for distribution, and agricultural organizations for networking and resources.
What should I include in my greenhouse business plan?
Your greenhouse business plan should cover market analysis, financial projections, operational plans, and strategies for customer engagement and growth.
How do I ensure profitability in my greenhouse business?
To ensure profitability, closely monitor your cost structure, diversify your revenue streams, and continuously assess market trends and customer preferences.
What resources are available for greenhouse farming?
Resources for greenhouse farming include agricultural extension services, online courses, local farming organizations, and comprehensive guides on financial planning and risk management.